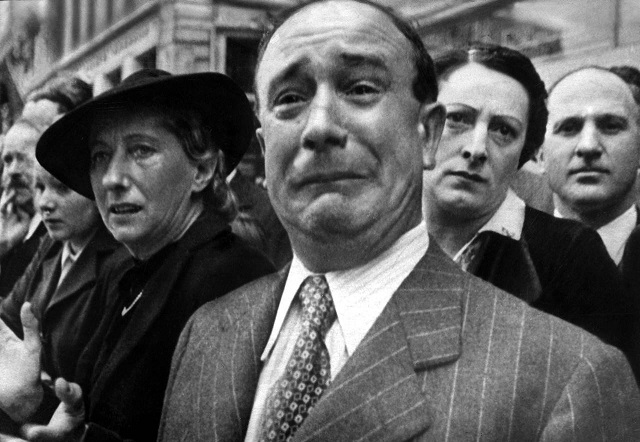
History 13/03/20 How life has changed in Europe after its occupation by Hitler
Reshaping the map of Europe during the Second world war, the Germans very selective in its population. If one were immediately sent to concentration camps, others from time to time allowed to enjoy life.
New order
in the first weeks of the occupation of Europe by the Nazis began to establish her “New order”, which provided various forms of dependence: from vassal (Hungary or Romania) – to the open annexation (Poland and Czechoslovakia). Finally, political and geographical boundaries of Europe were to disappear in greater Germany, and some people – wiped off the face of the earth.
the Nazi version of the European Union provided a different relationship to the enslaved countries. This was due to their “ethnic purity”, the cultural level and the degree of resistance provided by the occupation authorities. Under these conditions, a predominantly Slavic population of Eastern Europe has significantly lost to Western neighbors.
If, for example, annexed Polish territory was declared a German “Generalgouvernement”, South France self-governing collaborationist regime of Vichy. However, not always in Western Europe, the Nazi regime was a success. In the Netherlands and Belgium, the German agents were too weak, and therefore the German proteges Mussert and Degrell the population enjoyed popularity not.
In Norway according to statistics, only 10% of the population supported the occupation authorities. Perhaps it is because of the perseverance of the Scandinavians Reich created a special program to “improve the gene pool”, in which several thousand Norwegian women had children from German soldiers.
Europe without a war,
If the Western territory of the USSR has become a solid field of battle, the life of a significant part of Europe differed little from peace. In European cities Rhave Abuali cafes, museums, theatres, places of entertainment, people went shopping and rest in the parks. The only thing conspicuous is the presence of German soldiers and signs in German.
Especially in this regard was indicative of Paris, which the Germans appreciated because of the possibility of a relaxing holiday and fun.
At the Rivoli sported fashionista and cabaret weekends entertained local and visiting public. More than a hundred of the Parisian clubs was specifically opened to service the soldiers of the Wehrmacht. “I’ve never been so happy,” admitted the owner of a brothel.
In General, German policy in France was flexible and encouraging. Intellectual and creative elite here has given scope for action, certain concessions provided for various French institutions. So, if from other countries, the Germans in the huge number of exported values and Antiques, then, for example, the Louvre has reserved the right to prohibit the export of any work of art in Germany.
Without any restrictions worked in the French film industry. During the years of occupation in France was released 240 400 feature films and documentaries, as well as the many cartoon of the years that exceeded the products of Germany. Note that during the war blossomed talent of the future stars of world cinema – Jean Marais and gérard Philippe.
there were, of course, certain difficulties associated with wartime. For example, many Parisians with the butter and milk had to travel to the villages, part of the food products issued coupons, and some restaurants served only the Germans, were also introduced a ban on free sale of radios. However, these limitations did not go to any comparison with life in most cities in Eastern Europe.
workdays
Europe as a raw material appendage of Germany worked in the first days of the war – almost all its resources were switched to maintaining the power of the Third Reich and to ensure that rear bthe basics in the confrontation with the Soviet Union. Austria gave the iron ore, Poland – coal-Romania – oil, Hungarian bauxite and iron pyrite, Italy – lead and zinc.
a Big role was played by human resources. In one of the confidential notes of the German officials contained requirements “for most types of work that are simple, minor and primitive” actively use “support people”, predominantly Slavic origin.
to meet the needs of the Wehrmacht in many parts of Europe opened branches of German companies “Krupp”, “Siemens”, “IG Farbenindustrie”, pereorientirovanija local plants such as “Schneider-Creusot”, France. However, if the conditions of the workers of Western Europe were quite good, their Eastern colleagues worked on wear, to give Hitler promised profits, which “did not know the history”.
for Example, the average length of time that the employee works on the Polish plant “Bunawerk” does not exceed two months: every three weeks was carried out inspection work, the results of which the feeble and the sick were sent to the crematorium, and their place was taken by new victims of this monstrous conveyor death.
Ghetto
the Jewish ghetto is one of the unique reservoirs of life of Europeans during the Nazi occupation and at the same time an example of the amazing adaptability and survival in extremely adverse conditions. Stripping the Jews not only of all values and savings, but the minimum livelihood, the German authorities isolated them in the private parts of some major European cities.
the Actual life is difficult to call. Jews usually settled several families in one room – the average population density in the “cleared” under the ghetto blocks in 5-6 times higher than previous figures. Jews were forbidden here almost everything – trade, do crafts, learn and even to move freely.
However, through the holes in the fences, the Teens got into town and got a hundredl is necessary for the people “quarantine zone” food and medicine.
The largest ghetto was Warsaw, where he lived at least half a million people. Its inhabitants, despite the prohibitions, we managed not only to survive but to education, to cultural life and even to arrange leisure.
That the Warsaw ghetto was a hotbed of the largest anti-Nazi resistance in Poland. German authorities to suppress the uprising of the Warsaw Jews spent almost more effort than the seizure of Poland itself.
Concentration camps
In the occupied countries in the German sample of the new government created a network of concentration camps which, given the current data exceeded 14,000 points. Here in unbearable conditions contained around 18 million people, of which 11 million were destroyed.
For example, take the camp Salaspils (Latvia). The prisoners were huddled in 500-800 people in close barracks, their daily diet consisted of a 300-gram piece of bread mixed with sawdust and a Cup of soup from vegetable waste. The working day usually lasted at least 14 hours.
But the Germans created and exemplary of the camp, which was to show the world the German “progressive humanity”. This was the Czech “Theresienstadt”. The camp contained mostly European intellectuals – doctors, scientists, musicians, artists.
For some prisoners has created a family barracks. The camp functioned as prayer houses, worked as libraries and theatres, were exhibitions and concerts. However, the fate of many residents “of Theresienstadt” was sad – their lives ended in the gas chambers of Auschwitz.
Russian Seven
Source:
© Russian Seven
Recommended statesalaska… Share: Comments Comments on the article “How life has changed in Europe after its occupation by Hitler” Please authority certificateswhites to leave a comment! br>
Share on Tumblr