History 11/03/20 “Operation Buffalo”: why the Germans withdrew from Rzhev in the spring of 1943
on March 3, 1943, after a long fruitless fighting, the Soviet troops finally entered the town of Rzhev. But before them was a deserted city. Numerous German group of armies “the Center” unexpectedly left their positions.
“Rzhevskaya chopper”
In the historical memory of the battles of Rzhev were the most difficult and terrible period for all of the great Patriotic war. The Soviet soldiers called them “the Rzhev abyss” or “the Rzhev meat grinder”. Remembered with horror of the battles in “a large space of Rzhev” and German veterans.
the Second world war knows no bigger battle than Rzhevskaya battle: any number of troops involved — more than 10 million on both sides or area of coverage — eight regions or for the duration of fighting — 15 months (from January 1942 to March 1943), nor the number of operations — nine on each side.
the Total losses of the Soviet troops across the arc encircling Rzhev, according to historian Alexei Isayev, amounted to 1 160 787 people. How many Germans were lost, is not known, but only for the first three months of fighting, they had missed more than 330 thousand soldiers and officers.
virtually every patch of land near Rzhev was sprinkled with blood and littered with corpses. “Never been there it is difficult to imagine what is stinking in the summer sun mash-up, consisting of the worms is covered with thousands of human bodies,” recalled veteran Petr Mikhin.
What made the German and Soviet command to fight the depletion of the forces in the Rzhev bridgehead? German General Horst Grossman, Rzhev was called “the cornerstone of the Eastern front”, and in the diary of the former chief of staff of the German army Franz Halder described almost every day replete with references to Rzhev.
“Open the Rzhev is to open the road to Berlin,” kept repeating the German radio. And for the Soviet command Rzhevskiy springboard is first and foremost a great opportunity to push the Germans farther away from Moscow, and to intercept strategic initiative.
a Dangerous ledge
as a result of the Rzhev-Vyazemskoe th operation at the end of April 1942, was formed protrusion 200 km wide and 160 km in depth, occupied by German troops – about 2/3 of the size of the group of armies “Center”.
for a Long time the Germans managed to get hold of the ledge due to more favorable positions. Pre-equipped line of defense allowed the German troops to survey the approaches for many miles, while Soviet troops were forced to conduct their attack through the swampy lowlands under continuous shelling.
Often happened that the fortifications several times a day crossed one or the other belligerent. “Often oltransa was occupied by the Germans, and the other half we recalled one of the soldiers. – Annoyed each other in every way I could. Interfere with food intake: imposing fight and took the Germans lunch. In spite of the enemy bawled songs. On the fly catching grenades thrown by the Germans and then tossed them back to the owners”.
By mid-January 1943, a military unit of the Kalinin front liberated the city of Velikie Luki, which has increased the threat of encirclement German forces in the Rzhev salient. Given the complete defeat of the divisions of the Wehrmacht at Stalingrad and in the Caucasus, the situation of the German forces at Rzhev were very unreliable.
At the Headquarters of the 9th army understood that, in the absence of reserves, any tactical blunder and even a small numerical superiority of the enemy could lead to disaster, which could put an end to the aggressive plans of the Reich. Moreover, according to intelligence reports the potential threat of carrying up to 12 thousand partisans and red Army soldiers, cut off from their units and left in the German rear.
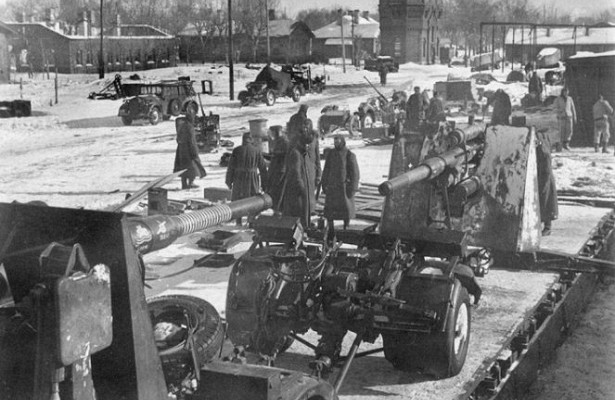
In these conditions, the previously planned operation on the withdrawal of German forces has become more urgent than ever. The challenge was serious: unbeknownst to the Soviet side to bring the 24 division – about 320 thousand soldiers and officers, more than 400 artillery pieces and 100 armored vehicles.
In turn, the Soviet command intended to use the chance. With the aim of entering the rear of the enemy force planned to cut down Rzhev protrusion to hold the encirclement and destroy the main forces of army group “Center”.
“Operation Buffalo”
a Final decision on the withdrawal of troops in prepared positions was signed on 28 February 1943. Responsible for implementation of operations under the code name “Buffel” (“Buffalo”) was appointed the commander of the 9th army of the General p. Apostol, who to Walter Model.
According to the plan of operation on the shoulders of the personnel of the Wehrmacht went to a number of challenges. Among them: creation of new lines of defense; construction of 200-km road for cars and 600-km toboggan run and horse-drawn transport; the evacuation of the farming (livestock, crop inventory, tools) and more than 60 thousand civilians.
the Most serious problem was the evacuation of the civilian population. General Friedrich von Mellenthin wrote that “old and young, healthy and sick, peasants and townspeople, all insisted on the evacuation, so powerful was the dread of the soldiers and commissioners of their own country.”
Soviet, Russian and even American historians deny the possibility of a voluntary evacuation of civilians. According to the American historian Stephen Newton, the order to evacuate local residents gave himself Model. “Soviet citizens were sent to forced labor in the construction of defensive lines. Also, wanted to avoid Subversion and sabotage during podgotovitelno about the period of the operation and the operation itself,” concluded the historian.
as a result of successfully performed operation the German command was able to release reserves that could be transferred to other areas of military operations. Included in the Rzhev Soviet units found in the city, only the rear guard of the 9th of Aria, to create a visible presence of the German troops.
the persecution of the troops of the red army onstopusa the German army was complicated by the well-organised defensive positions, minefields and destroyed communications. Greatly hampered the advance of the Soviet troops and the spring thaw began in mid-March.
the red Army covered a 7-km per day. In the future, deprived of their supply of ammunition and food, faced the resistance of the Germans, they were forced to stop the persecution. 30 Mar operation “Buffel” was completed.
These different results
“please Accept my warmest congratulations on the occasion of the liberation of Rzhev, – wrote to Stalin Winston Churchill. – From our conversation in August, I know how much importance You attach to the exemption of this paragraph”.
About the importance of the Rzhev operation indicates the visit of Stalin in the district of Rzhev in August 1943. However, the results of this victory were mixed. Although the enemy was thrown back more than 100 kilometers, the victory was achieved at the cost of huge losses and destruction.
In the fighting in the Rzhev and neighboring villages were almost wiped from the face of the earth: from 5443 houses Rzhev survived only 297, and 20 thousand were in the occupation of Soviet citizens survived only 150. According to estimates by the Extraordinary State Commission damage to the region amounted to half a billion rubles.
Rzhevskaya battle was considered one of the most unsuccessful operations of the red Army in the great Patriotic war. Its details were hushed up by Soviet historians, as well as the fact that the troops of army group “Center” themselves left the beachhead. Despite the intelligence reports, the Soviet command failed to timely respond to the retreat of German troops and missed the opportunity to achieve a decisive superiority. Guilty was recognized as General Laitinen t Konev, who with the wording “can not cope with the task management front” was dismissed.
the German retreat, on the contrary, was found to be successful. As a result of “operation Buffalo”, the Wehrmacht lost about 15 thousand soldiers while the total losses of the red Army pursuing German units exceeded 138 thousand.
Retreat freed divisions, which together with transferred to the Eastern front parts of France almost completely compensated for the loss of 6th army at Stalingrad. In recent times, Hitler had a real opportunity to seize the initiative and start a General offensive.
Source:
© Russian Seven
Recommended statesalaska… Share: Comments Comments on the article “Operation “Buffalo”: why the Germans withdrew from Rzhev in the spring of 1943″ Please log in to leave a comment! br>
Share on Tumblr