Weapons 09/03/20 The worst weapons in the Second world war
the Second world war became a proving ground for hundreds of new types of weapons. Opponents wanted to create their own “weapon of retaliation”, but in combat it is often not only had low efficiency, but also threatened those who had applied.
the Pistol the Nambu Type 14 (Japan)
Despite the fact that the Nambu pistol from the 1920s to 1940-ies was the main personal Goianapolis Imperial army, he is considered one of the worst automatic pistols of WWII. Nambu had low fire power was heavy and awkward to use. A special feature of its design was the ability to produce fire before the breech part of the weapon was locked. Because of this accidental touch of the trigger often led to spontaneous shot. No wonder it was considered that the Nambu is more dangerous to its owner than to an enemy.
Heavy flamer Grossflammenwerfer (Germany)
Heavy German flamethrower of world war II consists of a conventional cylinder supplied with compressed gas cylinders, and straps to hand-carry. This design with curved outlet pipe is connected to the hose. The weight of the flamethrower demanded a settlement, consisting of at least two people.
because of the high danger carried this “liquid bomb” in the calculation is usually assigned to criminals or deserters. Military anti-Hitler coalition considered Grossflammenwerfer barbaric weapon and was using his Wehrmacht soldiers to take no prisoners.
submachine Gun STEN MK II (UK)
This weapon is a firing range of 70 meters and a capacity of 32 cartridge was commissioned by the British military in 1940. To the disappointment of the British soldiers of the mechanism of the gun STEN was slightly undone and very often did not work. In addition, the report reported of bullets at the shooting range bounced off the targets.
a British expert in the field of military security Jill Dohert, trying to justify bad development, wrote: “At the time, Britain tried to seize, and had a large number of weapons, STEN quickly and easily assembled, and it was much better than nothing.”
Krivostvolny weapon (Germany)
In 1943, the Wehrmacht officially adopted the device for firing from cover Krummerlauf (“Bent barrel”). It was a standard assault rifle with an attached curved trunk, periscopic sight, with a capacity of 30 rounds and a firing range of 2 kilometers, which was supposed to fire from cover at an angle of 30 and 45 degrees.
the Soviet soldiers called this gun “the treacherous”, which is “for the cowardly shooting from the corner”. The idea was promising, however, to bring it properly to life failed. Having spent a lot of time and money to design Krummerlauf, the German developers decided that the serial production rifles will fly to the penny, and the efficiency will be extremely low.
“Bazooka” (USA)
EN Masse anti-tank hand grenade M1, the Americans began to use since 1942 in the North African campaign. It was a single rocket launcher with explosives, weighing 1.5 kg and a range of 150 meters. One of the problems with “Bazooka” – a powerful flash that could pour arrow fire. Later models of the rocket launcher already had the rear armoured shield.
Another problem is more serious. “Bazooka” was only effective at short distances, however, the American Marines, it was extremely difficult to get close to the tank of the enemy in the desert. For the time of the Second world war was not a single recorded case of destruction of the tank “Bazooka”.
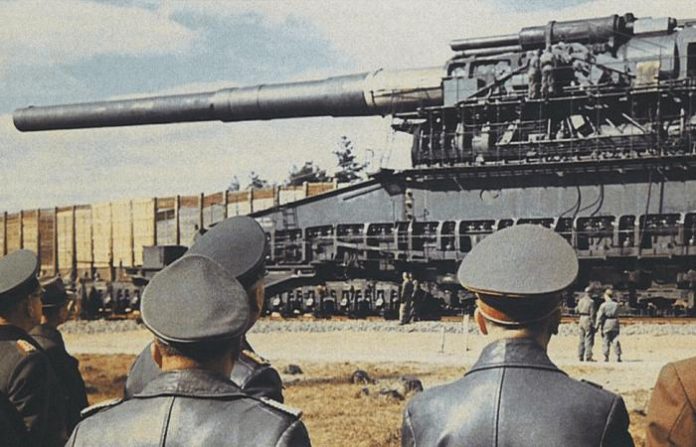
“Gustav” and “Dora” (Germany)
Two supermassive German guns with a caliber of more than 80 cm “Gustav” and “Dora” was supposed to intimidate the enemy, but to inflict significant damage. These giants, which had no analogues in the world, could only be carried in parts. Assembly, installation and operation of cannons were made in the prepared place involving unimaginable number of staff – about 4,000 people.
two guns only “Gustav” took part in the battle. During the siege of Sevastopol in 1942, he made 42 shot shells weighing in at 4800 pounds each. German military expert Alexander Ludek called giant cannon “technological masterpieces”, but said that they are “in fact a waste of materials, technological expertise, and human resources.”
“the V” (Germany)
the Third Reich launched the first cruise production of ballistic missiles in the hope that this latest weapons can turn the tide of the war. It all began in 1943 with “V-1”, database deployment, which were placed in the North of France. The purpose of the missiles was the British Isles, particularly London.
Until the end of the war the British capital was released about 10 thousand such warheads, however, the lack of agility prevented many of them to reach the destination. 25% “V-1” were destroyed by British aircraft, 17% of anti-aircraft artillery, 20% of the shells failed to reach the Islands and fell into the sea. In addition, every fifth missile failed to launch.
Next was “V-2”, made the first suborbital flight, usmivki to a height of 188 miles. But in combat roles because of the low accuracy of the missile has shown itself to be weak: only about half of the launched shells fell in the designated area with a diameter of 10 kilometers. About 2 thousand preparing to launch “V-2” exploded before the start or immediately after it.
Minister of Germany’s armaments albert Speer in his memoirs, called the creation of “V-2” mistake. In his opinion, should not have to waste limited resources that were available to the Reich at such an expensive and ineffective project and use them to create anti-aircraft missiles to protect the German cities from bombing of sousnikeV.
Despite the failure of two models, the “V” in Germany and the third came, but this time not a rocket, but heavy gun, Vergeltungswaffe (or “English cannon”). Another “weapon of retribution” with a length of 124 meters, a caliber of 150 mm, weighing 76 tons was mounted directly into the hillside. Like its predecessors in the line of “V” the supergun was supposed to send shells across the channel.
“V-3” worked on the principle of multithread, code, successive detonations dispersed the projectile as it moves its trunk. The maximum range of the warhead was 93 km. Built from two samples, only the second cannon was used in battle. From 11 January to 22 February 1945 she fired 183 shells on just-released the Monaco, however, the effectiveness of fire was extremely low. 142 managed to fly to the target the projectile has claimed the lives of only 10 people.
the Plane kamikaze the Yokosuka MXY-7 Ohka (Japan)
By the autumn of 1944 the Japanese were also able to create weapons with a rocket engine, with which they were going to fight with the U.S. Navy. It was the plane kamikaze “Oka” carrying 1000-pound bomb, which was lifted in the air another more powerful machine – Mitsubishi G4M. After undocking from the rocket, the kamikaze pilot was in planning mode to bring your plane-projectile as close as possible to the target, then turn on the rocket engine and RAM the ship.
the Us Navy pretty quickly got used to neutralize the rocket threat. The launch range of “Oka” was much less than the radius of fighter cover carrier battle groups, and therefore, most of the Mitsubishi G4M and got lost on the approach, and not having to release the projectile. Once the rocket-kamikazes managed to sink the American cruiser.
“non-rotating projectiles” (UK)
Its part in the missile weapons of the Second world made by the British. “Non-rotating projectiles” is anti-rockets with wires attached and parachutes that were supposed to create in the air, the likeness of a minefield. While the shell slowly descended, he threatened for flying a number of aircraft that could snag the wire, pull the missile to the hull and explode.
However, in reality, “non-rotating projectiles” the main danger is not the enemy. A small change in the strength and direction of wind missiles could plan on the ship, from which they were launched. Despite the risk of a suicide bombing the British decimal fraction intensively used this weapon in the first days of the war.
Crawler mines “Goliath” (Germany)
With remote-controlled tracked vehicles “Goliath” the Germans were able to deliver almost any purpose, including armored vehicles, crowds, buildings or bridges, 66-pound bomb. Only in 1942 was made more than 4600 “Goliaths”, including carrying the 88-pound mines.
To the disappointment of the Germans self-propelled mines proved to be extremely cumbersome, unwieldy and difficult to manage. In addition, the toy was too expensive (from 1000 to 3000 Reichsmarks) and vulnerable to any anti-tank weapons. However, the Germans persistently used the “Goliaths” until the end of the war.
Taras Repin
Source:
© Russian Seven
Featured articles Share: Comments Comments on the article “The worst weapons in the Second world war” Please log in to leave a comment! br>
Share on Tumblr