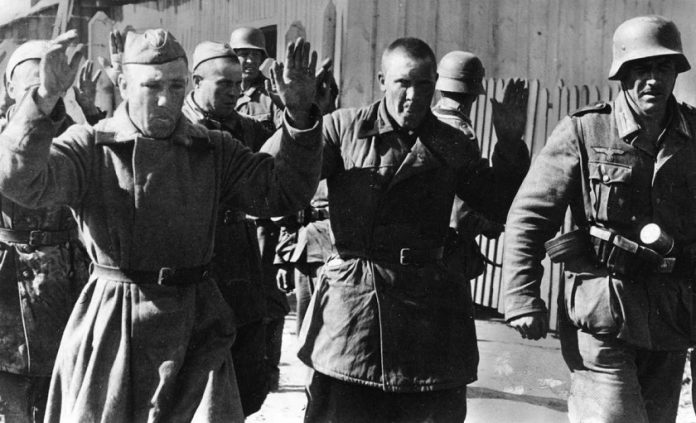
History 25/03/20 the worst defeat of the red Army in the Great Patriotic
in 1941 and the first months of 1942 was overshadowed by painful lesions of the Soviet Union from Germany. Despite a number of won battles that slowed the enemy’s advance, then, until the turning point in the war was far away.
the Bialystok-Minsk the battle of
This is the first and the biggest clash of Soviet and German troops summer months of 1941, which lasted from 22 June to 8 July. From the German side it was attended by more than 1.4 million military with the Soviet – about 790 thousand, but the number of guns, tanks and airplanes of the red army superior to the enemy.
the Plan of the German troops was a powerful attack from the flanks in the center of Minsk, the forces of the 2nd and 3rd Panzer armies to encircle large Soviet grouping. Tactics like “ticks” with strong flanks, weak center will be peculiar to the military doctrine of the Wehrmacht throughout 1941. In addition, the command of the Luftwaffe planned to win a crushing victory in the air, thereby depriving the Soviet aviation opportunities for full resistance in the future.
the Most weak section of the front near Brest, where the Soviet units with the exception of defenders of the Brest fortress was destroyed in a matter of days. Attempted a powerful counter-attack, which the Soviet commanders had intended to not only reject, but also to defeat the enemy, failed, and resulted in two “boiler” – Bialystok and Minsk.
the German troops during the Bialystok-Minsk battles managed to move 300 km deep into Soviet territory, was captured more than 320 thousand soldiers and officers of the red Army, the Western front was almost completely destroyed.
the Battle near Vitebsk
After the defeat of Soviet forces in the Bialystok and MInskoy and the “pot” German troops headed towards the rivers Western Dvina and Dnieper river, after crossing which they have opened the road to Moscow. Given that, the German connection, moving to the East, stretched for tens of kilometers, the Soviet commanders had the opportunity to defeat the enemy in stages.
in Order to stop the advance of those German groups in Vitebsk, Marshal Timoshenko decided to strike a counterblow by the forces of the 5th and 7th mechanized corps at Lepel district, however, due to the lack of consistency in the actions of the Soviet command powerful attack came down to a number of small, scattered clashes.
This delay allowed to transport across the Dvina, a significant part of the German motorized formations and to create a strategic advantage. “The crossing of the Western Dvina between the Beshenkovichi and Ulla three divisions of the 39th Panzer corps and the mastery of Vitebsk had a decisive significance for the entire operation,” later wrote Lieutenant General Pavel Kurochkin.
which Lasted from 6 to 10 July in Vitebsk, the battle cost the Soviet tankers large losses: 5th and 7th mechanized corps lost over 800 tanks and a substantial part of the personnel. According to the official version, during the battles of Vitebsk captured by the Nazis was Stalin’s son, Yakov Dzhugashvili. As a result of defeat in the Soviet defense was breached, through which German troops reached the Moscow highway.
the Kiev defensive operation
for Two months, from July to September, 1941, lasted a bloody defense of Kiev, where the Soviet side was attended by troops of the southwestern front and the Pinsk flotilla under the overall command of Marshal Semyon Budenny, with German army group “South” under the command of field Marshal Gerd von Rundstedt.
Concentration of Soviet troops near Kiev paralyzed the further advance of the German army that was planning to go to INDUindustrial areas of Donbass. For the German command it was important not only to break the Kiev defensive line, but also to prevent the escape of large parts of the red army deep into their territory.
Quite a long time in the area of the Kiev fortified area, Soviet troops quick counter-attacking raids slowed down the enemy on the outskirts of the Ukrainian capital. This changed dramatically when the German command decided to throw at Kiev troops of army group “Center”, temporarily halting the plans for the attack on Moscow.
as a result, by the 20th day of September, German troops managed to break the resistance of the South-Western front and go to Kiev. According to the data released by the General staff of the Russian Armed Forces in 1993, Soviet troops during the Kiev defensive operation has lost more than 700 thousand people, of which 627 thousand irretrievably.
Vyazemsky boiler
By the end of September 1941 the German command has developed plans to seize the Soviet capital. After a major regrouping of troops, the Germans hoped to break the line of defense of Moscow to encircle and destroy the troops of the Western and Bryansk fronts.
the Soviet General staff had expected that the enemy will intensify offensive operations along the direction of the Smolensk – Vyazma on the junction of 16th and 19th armies. Here were concentrated the main forces of the red army. However, the Soviet command had miscalculated: the Germans struck North and South of the intended direction.
the advance of the German troops was so powerful that the Rate of the Supreme Commander decided to withdraw the troops to the Rzhev-Vyazemsky defensive line. In some parts of the front in a matter of days the Germans managed to break into the defensive ranks of the defenders of 50-80 kilometers. In the area of Vyazma, Soviet forces were surrounded, where fights were resistant to 13 of October.
the Total for the Soviet command was poor. The result of Vyazma “pocket” losses of the red army killedfired and wounded amounted to 380 thousand people, more than 600 thousand were captured.
the Crimean disaster
In December 1941 – January 1942, the Soviet troops managed to return earlier captured the 11th army of the Wehrmacht Kerch Peninsula, but attempts to further the liberation of the Crimea, they suffered heavy losses, and concentrated solely on defense.
the German command noticed that on one of the sections of the defensive line between the Black sea and Coy with Hassan, Soviet troops had limited power. It have guided the development of the plan of operation “Hunting bustards”.
7 may German forces as a result of sudden and massive air strikes were able to put the defenders of big losses. And on may 8, after powerful artillery fire began the offensive. Despite the fact that the Soviet group of forces in numbers was superior to the German – 250 thousand compared to 150 thousand, due to inept command, she suffered a painful defeat, thereby exposing the danger of the invasion of the Caucasus direction.
Soon after the defeat at Kerch weakened and the defense of Sevastopol. As a result of almost complete blockade of the city and, as a result of the lack of sufficient ammunition the defenders had nothing to counter devastating raids and attacks from the sea the German troops. On 3 July 1942, Sevastopol was lost.
the Second battle of Kharkov
After repelling the offensive of the German troops near Moscow, the General staff decided to start active actions in other areas. This contributed to the build-up of military industry and the establishment of reserve armies. On the background of the success was planned and the Kharkov offensive operation, which, however, turned into a complete encirclement of Soviet troops.
the Strategic plan of the Soviet General staff implied through a series of operations to force the enemy to spray their reserves, giving him no opportunity to create a strong gruperointernals to attack in a particular direction. However, the may offensive of 1942, Soviet troops near Kharkov by the Germans was successfully repulsed, and after that organized their own counter-offensive.
on may 28, by order of Marshal Timoshenko’s offensive operation has been cancelled: now all efforts were directed to the re-opening of a circle created by the German group. Despite the desperate attempts by Soviet troops to break through the encirclement, only a tenth of coped with the task successfully. The operation cost the lives of 270 thousand Soviet soldiers. At the end of may Panzer army Hermann Hoth broke through the defenses between Kursk and Kharkov and turned to don.
Taras Repin
Source:
© Russian Seven
Featured articles Share: Comments Comments on the article “the worst defeat of the red Army in the Great Patriotic war” Please log in to leave a comment! br>
Share on Tumblr